Mushrooms are fascinating life forms: they have a mode of development of their own that is unlike any other type of individual. In the great animal and plant kingdom, they can be an essential link: they communicate, for example, with trees in forests to create a unique network.
We humans like to spend time picking them during our country walks and use them most of the time in the kitchen. Rich in vitamin D, they are tasty and have a multitude of benefits for our body. In risotto or pan-fried, we find them in many dishes that we enjoy.
However, apart from their use in cooking, a certain type of mushroom is also used: those called hallucinogenic mushrooms or magic mushrooms. These mushrooms get their nickname from their psychotropic effects. They have several types such as Amanita fly or Cleviceps Purpurea, in other words ergot, from which LSD is derived or Psilocybe mushrooms, the best known.
Description of hallucinogenic mushrooms Psilocybe
They differ from another genus of mushrooms by the presence of psychoactive substances, including psilocybin and psilocin.The presence of one of these substances, psilocin, creates a blueness when picked, due to oxidation.
Depending on the species of mushroom, their appearance can vary: sometimes dressed with a thin foot, sometimes with a thicker silhouette, wearing a brown hat or a more orange hat.
They can sometimes be confused with dangerous poisonous mushrooms that are not psychotropic. It is therefore necessary to pay close attention to their identification.
Where do they grow?
Some species of hallucinogenic mushrooms such as Cubensis are grown indoors, while others are grown outdoors.
They can adapt to different climates. Thus they can be found in different regions and different countries: Asia, America or Europe. Most will be found in the north of these continents, but some species have managed to adapt to drier climates, such as central Spain, or wetter climates, such as Mexico.
They can also sometimes be found in feces or manure, which mushrooms are particularly fond of.
Like all mushrooms, you have to keep an eye, be attentive and remember the places where they grow!
How do they work?
Psilocybes hallucinogenic mushrooms contain psilocybin, psilocin but also baeocystin and norbaeocystin, which are two tryptamines generally considered less active than the first two substances. For example, P .Semilanceata contain about 1.70% psilocybin, 0.02% psilocin and 0.36% baeocystin when dried.
Psilocybin is a prodrug of psilocin: after eating mushrooms, psilocybin is degraded and turns into psilocin, so the latter is the only one of the two substances to interact with our brain.
Psilocybin and psilocin have similar structures to the neurotransmitters serotonin 5-HT. Most hallucinogens act specifically on a subtype of these neurotransmitters – 5-HT2. It is thought that it is from this mechanism of action that hallucinations and psychedelic effects originate.
However, it is not the only genus to contain these precious substances since there are also Panaeolus, Conocybe or Gymnopilus.
The Fly Amanita, which is also a mushroom considered magical, is not a Psilocybe. It does not contain psilocybin or psilocin, but muscimole and ibotenic acid, which are these two main active substances.
The desired effects
There are three different types of drugs, with specific effects and risks: stimulants, those that keep you awake and give energy, depressants, which will tend to calm down, and psychedelics or hallucinogens, which change reality by creating hallucinations and acting on different senses. Some drugs can be classified into several categories, such as MDMA which is an stimulant and a psychedelic.
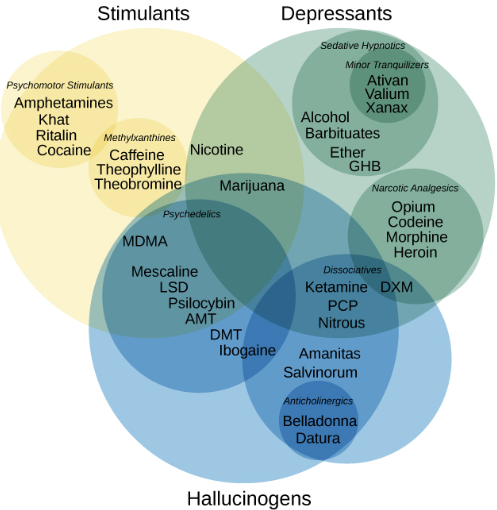
Hallucinogenic mushrooms are mostly psychedelics but they also have a depressant side: unlike its cousin LSD, mushrooms will have a calmer side, although also having euphoric effects. Especially during the climb, the consumer may feel heavier, as if lacking physical energy, and will tend to rest out.
Regarding the effects, the consumption of hallucinogenic mushrooms alter all known senses (hearing, sight, touch ..) But also balance, the placement of one’s body in space or the feeling of pain and heat, which are generally senses to which we pay less attention. Time can pass very slowly or very quickly, short-term memory is shortened and messy, the mind can start to make so-called “mental loops”, which can give rise to comical situations or on the contrary anxiety-provoking.
The effects depend on the dose and therefore on the intended use and condition. At low doses, the consumer will have a slight physical feeling, an intensification of colors, a desire to laugh or a new way of thinking and seeing problems.Some people use mushrooms for example to solve different problems thanks to the step back they offer. Although an anxious state may already appear at this intensity, it is less likely than at high or medium doses.
At medium doses, the effects are more present. Longer-term memory is affected, hallucinations begin to affect all the senses: patterns and scenes form with eyes closed or eyes open. Some surfaces may begin to move more or less slightly. Thoughts are accelerated and the way of thinking is impacted in a more pronounced way. We feel emotions in a strong way and new links between our ideas are formed.
At high doses, the effects are further enhanced. The ego, namely the representation and consciousness that one has of oneself, is very impacted, up to its total dissolution. It is often reported the complete or partial disappearance of his memories. Hallucinations are very engaging and surround the consumer, which can cause him to lose all connection with reality.Travelers also report an ultimate connection with the entire universe, a state of rebirth or the meeting of entities.
Regarding synaesthesia, in other words the link between several senses (see sounds for example), it remains rare and often occurs at medium or high doses. This condition is much more present in people who have basic synaesthesia, without consuming any substance.
A dose of hallucinogenic dry mushrooms is usually between 1 and 5 grams (to be multiplied by about 10 for fresh mushrooms). Obviously, the dose depends on the tolerance and experience of each. Not all mushrooms are concentrated identically, even from the same species or harvest. It is therefore necessary to be careful about the dosage.
Side effects
The use of hallucinogenic mushrooms involves risks, including a list of side effects and a change of state. Mushrooms are made of organic matter to digest, consuming them usually causes more stomach aches and digestive problems than other substances. To overcome this, some consumers infuse them in hot water to make a tea.
A slight or moderate increase in heart rate may also be observed, especially if the situation becomes anxiety-provoking.
The consumer may experience muscle pain or cramps, dizziness, changes in temperature feeling (shivering then heat stroke) due to vasoconstriction, or recurrent yawning.The eyes are usually slightly moist and the pupils dilated.
He may also have the possibility of a “bad trip” which can manifest, among other things, in the form of a panic attack and can lead to dissociation. It is important to take care of your environment (place, people around us ….) and their mental health before and during taking to try to avoid that.
The different species
Cubensis
Fr .Cubensis is the most widely grown hallucinogenic mushroom indoors. It can often be found in kits, ideal for beginners, or in the form of spores, in impressions or syringes.


- Mckennaii growkit

Mckennaii growkit
The Psilocybe Cubensis Mckennaii spores are named after the famous Terence [...]44.00€Voir le produit - MycoSpores Psilocybe Cubensis Colombian

MycoSpores Psilocybe Cubensis Colombian
Vial of Psilocybe Cubensis Colombian spores already mixed in 5ml of liquid culture.The [...]25.00€Voir le produit
They need a temperature between 25 and 28 degrees during the colonization phase, 23 to 25 degrees during the fruiting phase and a constant humidity around 90%.
They are easy to grow, hence their popularity, but can be less concentrated than other types of hallucinogenic mushrooms with, on average, 0.63 mg/g psilocybin and 0.60 mg/g psilocin.
There are several known varieties: B+, Golden Teacher, McKenaii… From one variety to another, they can look visually similar sometimes. Their concentration levels of active substances are substantially similar and therefore produce the same effects.

There are, however, certain types of P.Cubensis differ visually and are known to be more concentrated, such as the Penis Envy variety.


- Penis Envy [PE] - Growkit 100% Mycelium
![Penis Envy [PE] - Growkit 100% Mycelium](https://mycotrop.com/2561-cart_default/1.jpg)
Penis Envy [PE] - Growkit 100% Mycelium
Penis Envy [PE], psilocybe cubensis growkit made by Mycotek. 1200cc.100% [...]55.00€Voir le produit - Yeti - Growkit 100% Mycelium

Yeti - Growkit 100% Mycelium
Yeti , psilocybe cubensis growkit made by Mycotek.1200cc.100% [...]55.00€Voir le produit - Koh Samui Classic - Growkit 100% Mycelium

Koh Samui Classic - Growkit 100% Mycelium
Thai Koh Samui Classic, psilocybe cubensis growkit made by Mycotek. 1200cc. 100% [...]55.00€Voir le produit
Azurescens
The P.Azurescens are hallucinogenic mushrooms that have a thin foot and a light brown cone hat. They are best grown outdoors in wet weather. They are available in spawnkit, to install at home in your garden. However, their cultivation time, about 6 months, is longer than Cubensis.


- Psilocybe Azurescens Spawn Growkit

Psilocybe Azurescens Spawn Growkit
IN STOCK ! Contains one box of spawn form the Psilocybe Azurescens Astoria Mushroom [...]32.00€Voir le produit
Their main asset for consumption is their higher concentration of psilocybin and psilocin (respectively about 1.78 mg / g and 0.38 mg / g) for more powerful effects. They also require less regular maintenance than Cubensis and grow easily in the corner of the ground, if you follow the growing instructions.

Semilanceata
This species of hallucinogenic mushroom is often picked by consumers. It can be found in plains or grasslands and is particularly fond of soils fertilized by livestock. They are easily found in Europe, especially in the north and wetter climates.
It is recognizable by its long stem, its color that changes according to humidity, its moist texture to its central papilla. It is close in appearance to Mexicana.

Cyanescens
Fr .Cyanescens can be grown outdoors, it is particularly fond of wood debris, such as P.Azurescens. It can be found in urban areas but also in coniferous forests, usually in warm and humid environments. It is recognizable by its yellowish, brown or wavy bronze hat and white foot.


- Psilocybe Cyanescens Spawn Growkit

Psilocybe Cyanescens Spawn Growkit
IN STOCK ! Contains one box of spawn form the Psilocybe Cyanescens [...]32.00€Voir le produit
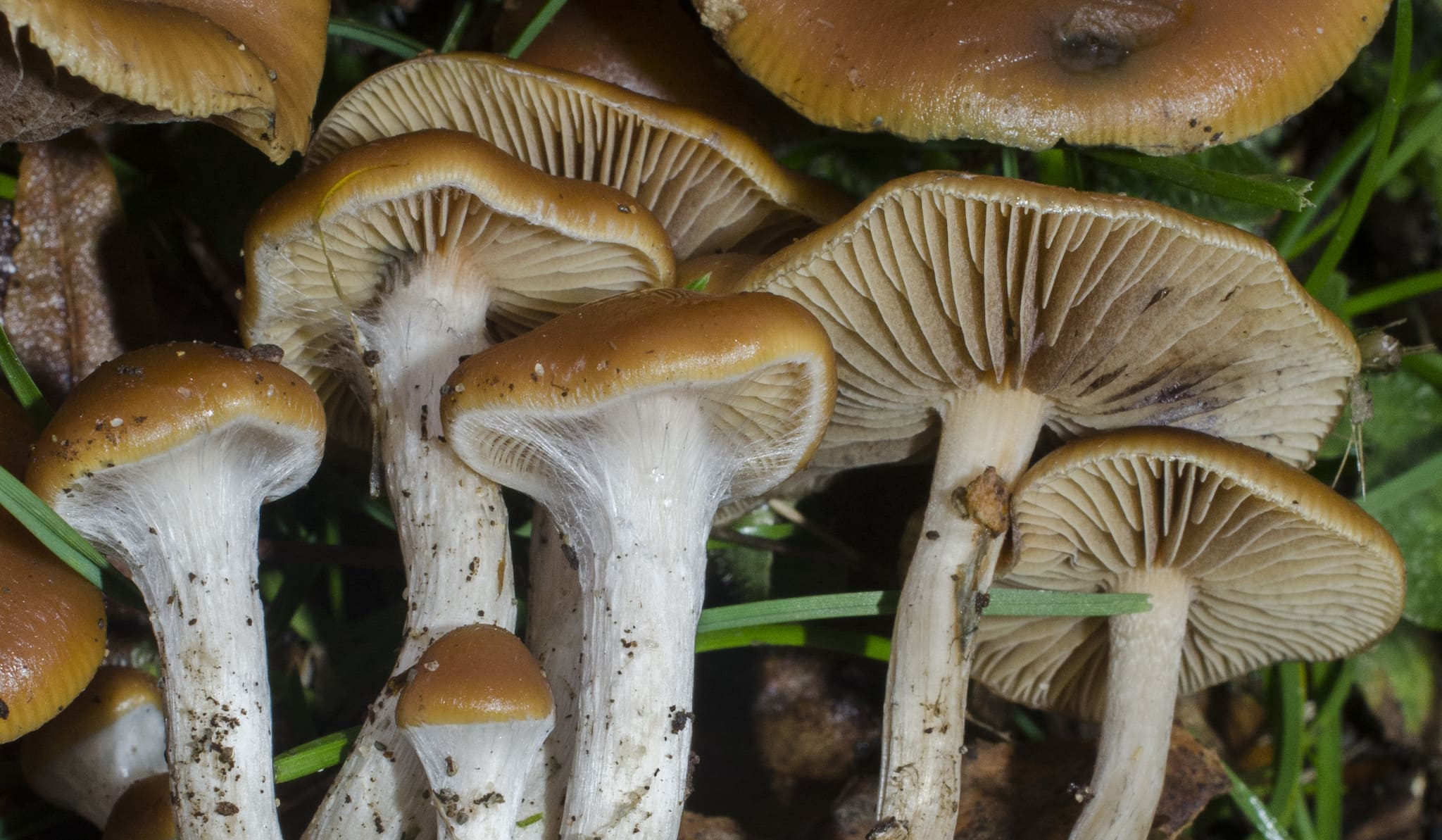

Other psilocybin-free hallucinogenic mushrooms: fly agaric and ergot
The Amanita Fly Killer, known as Amanita Muscaria, is rooted in popular beliefs as a dangerous but also easily recognizable mushroom, with its bright red hat and white dots.
Although it has been cooked detoxified in the past in some parts of the world, Amanita Tue-Mouches is best known for its psychotropic and hallucinogenic effects as well as its side effects that it can cause: nausea, stomach aches, vomiting …
The toxic dose of Amanita Muscaria is about one cap and the lethal dose about fifteen: however the content of active substances can vary greatly between each specimen of it. Most poisoning deaths are actually due to other types of Amanita.

Rye ergot is a fungus that uses rye and other grains as a host. It is known to have infected many people in the past, including rye. Ingestion of this fungus causes ergotism, inducing hallucinations, vomiting, severe vasoconstriction and spasms.
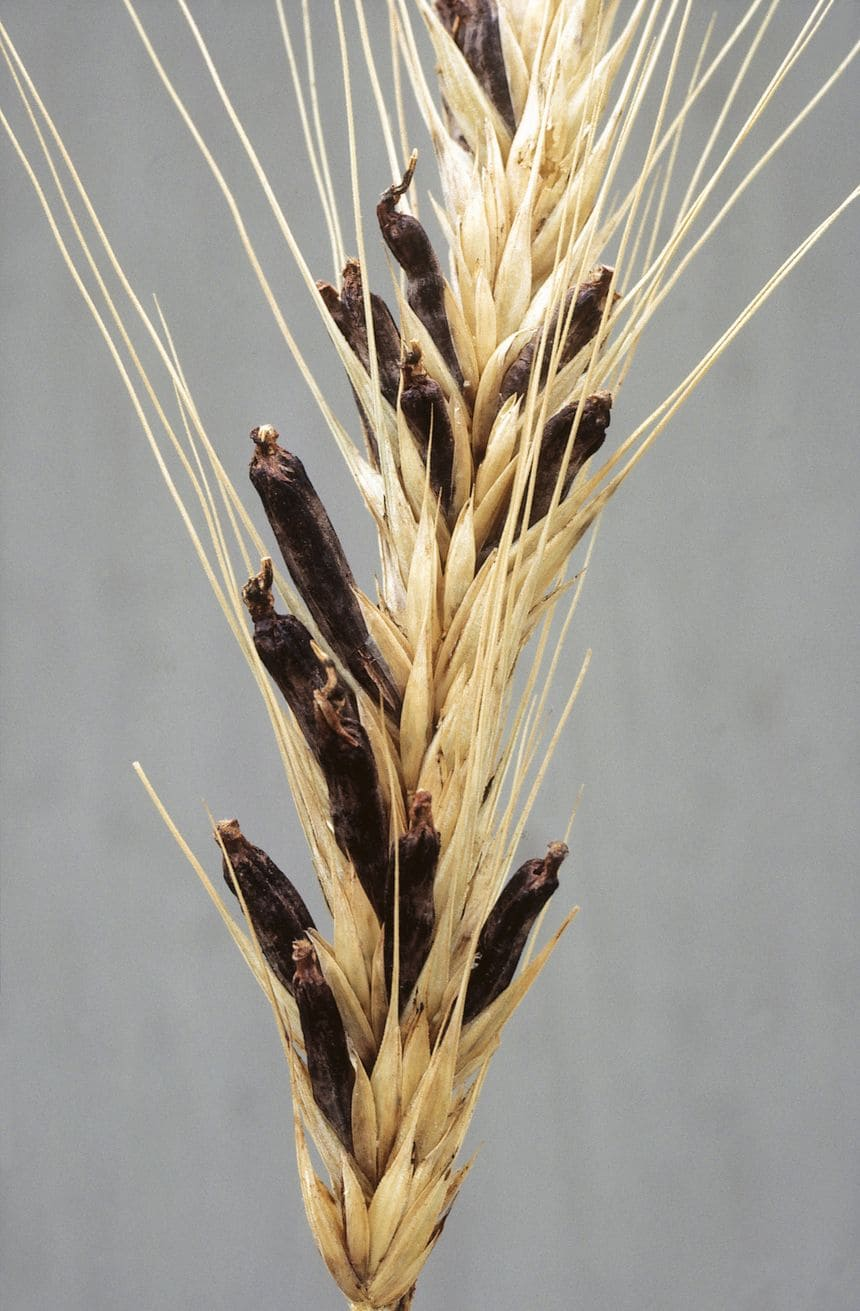

History records regular episodes of ergot poisoning, called “burning evil” during the Middle Ages. The symptoms were associated, at the time, with demonic possession. However, throughout history, ergot was also previously used to assist childbirth as it was likely to increase contractions of the uterus.
Rye ergot contains alkaloids that begin to be isolated at the very beginning of the nineteenth century. Subsequently, in 1938, Albert Hofmann succeeded in synthesizing a new substance, LSD, from lysergic acid: this is why the effects of LSD and hallucinogenic mushrooms are close.
The history of Psilocybe mushrooms
We find the first traces of hallucinogenic mushrooms a long time ago. In North Africa, several cave paintings have been found representing them dating from 7,000 to 4500 BC: more than 9,000 years ago.
Although they are traced in several places on the planet, they are most common in Mexico, with about 80 different species of hallucinogenic mushrooms. They were and still are used during rituals. As early as 1000 BC, pottery and other objects show that certain populations worshipped mushrooms.
In the sixteenth century, the Spaniards who came to conquer South America discovered for the first time these mushrooms and described them in books. Subsequently, cases of unintentional ingestion were reported in the United Kingdom and the United States.
Western discovery
It was not until the early nineteenth century that Westerners took a closer interest in hallucinogenic mushrooms. The botanist Richard Evans Schultes traveled in 1938 to the state of Oaxaca in Mexico to collect specimens of fungi, among them, P.Cubensis. Subsequently, anthropologist Jean Bassett Johnson will be present during a ritual ceremony during which a healer consumes mushrooms: he will then write several articles on this subject.
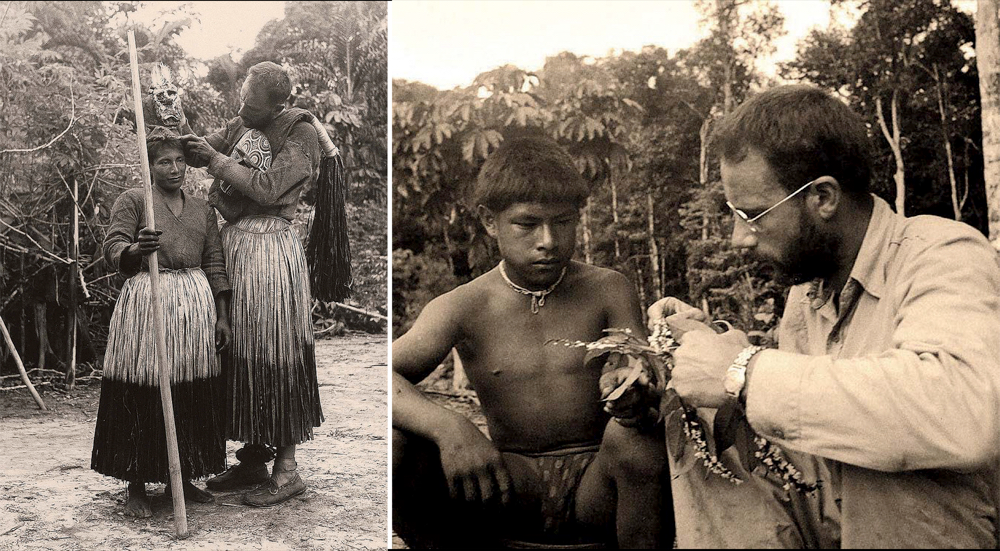

After this first momentum, a documentary by Pierre Thévenard will be made and then the book Hallucinogenic mushrooms in Mexico will follow, with about 40 articles between 1956 and 1972 on the subject. In 1957, Albert Hofmann isolated psilocybin: the Sandoz laboratory, for which he worked, sold the substance in the form of ampoules and capsules.
In this period, many artists experimented with hallucinogenic mushrooms, which inspired them in their creation, such as the famous writer of the book “Brave New World“, Aldous Huxley.
Although the Western discovery was made at that time, Psilocybe mushrooms , growing in large numbers on the American continent, were already used by many peoples through their religion and had worshiped them for more than 2000 years.
Legislation and Current Use: A Public Health Issue
Hallucinogenic mushrooms contain psilocybin and psilocin, both of which have been listed in Schedule I of the United Nations Convention since 1971 and are considered narcotics.
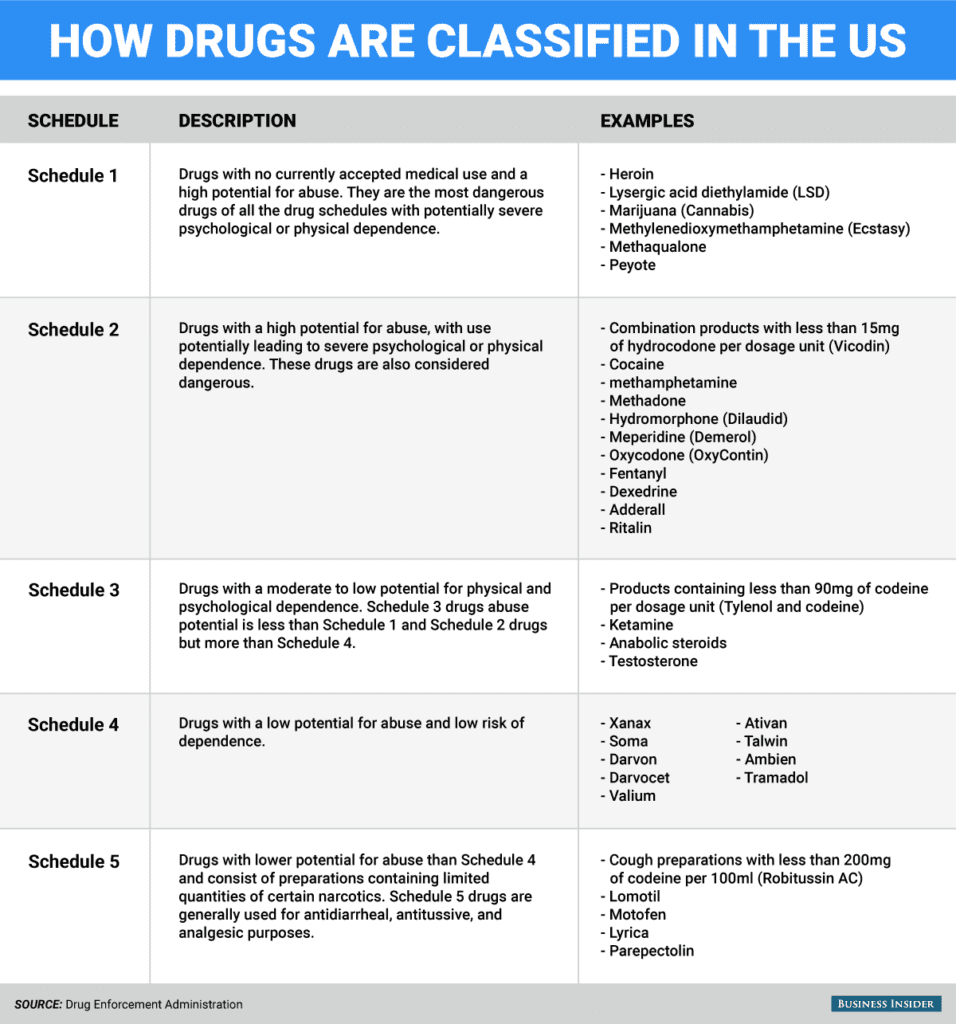
It was in the wake of The War on Drugs that the United States lobbied to ban a large number of substances, including LSD and mushrooms.A major campaign to ban and demonize various drugs, supported by US President Richard Nixon, began, destroying all studies and the therapeutic potential of these substances, such as MDMA or psilocybin. It would take more than 30 years for medicine to take a new interest in these substances and consider them as potential drugs.

In France, hallucinogenic mushrooms are classified in the list of narcotics: their consumption and possession are prohibited.
However, the law is backtracking in several countries. Portugal, Spain and a number of states in the United States decriminalize the possession of small amounts of mushrooms. The popularity of the latter is growing as the population realizes their therapeutic aspect: their role in the public health debate is once again being questioned.
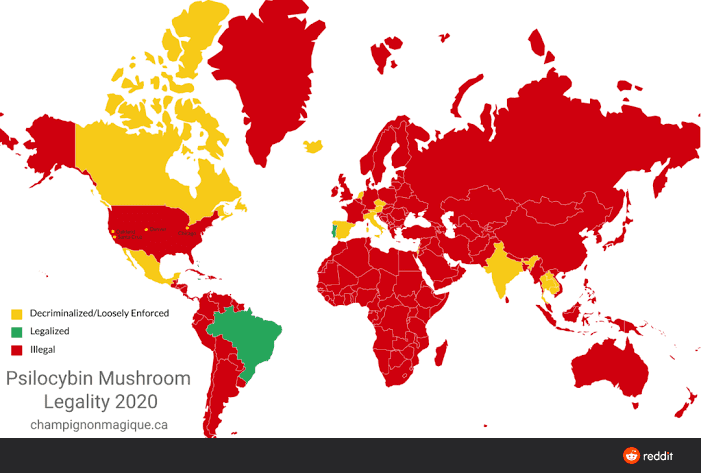
Hallucinogenic mushrooms have already been proven in scientific studies to help patients with depression, alcoholism or obsessive-compulsive disorder. We do not yet know well the mechanisms of action that come into play but taking a step back, being able to get out of one’s usual mental loops and neurogenesis seem to play a certain role.
Micro dosing or complete plug?
The consumption and dose of magic mushrooms depends on each individual: the purpose of the intake, the environment, the state of mind and the potency of the mushroom in question.
Nevertheless, there are two known modes of intake: micro-dosing and complete intake. Microdosing corresponds to a dose where the effects are imperceptible and does not change the state in a noticeable way. This dosage is generally part of a treatment in a therapeutic approach, self-improvement or search for creativity for example. There are several intake plans to consume in the form of micro-dosing, regardless of the variety: one day of taking, one day of observation, one or two days of rest and then repeating this cycle for several weeks is a fairly popular plan.


- Microdosing StarterKit

Microdosing StarterKit
With the aid of this accurate pocket scale and scalpel you are almost ready to start your [...]20.00€Voir le produit - Microdosing truffles Mexicana 10G

Microdosing truffles Mexicana 10G
Microdosing at his finest! Our new line of microdosing with very handy 1 gram pouches [...]14.00€Voir le produit - Microdose Magic Truffle - Microdosing XP

Microdose Magic Truffle - Microdosing XP
A natural way to relax and realise Research indicates that periodic microdosing helps to [...]14.95€Voir le produit
In this case, it is important to find the ideal dose: it is usually around 0.3 grams, or between 1 / 5 and 1 / 20 of a “full” dose. However, studies contradict each other on the effectiveness of this practice: some announce that the use of micro-dosing improves mood, creativity and well-being, while others see little or no improvement and that a larger dose should be taken to see noticeable effects.
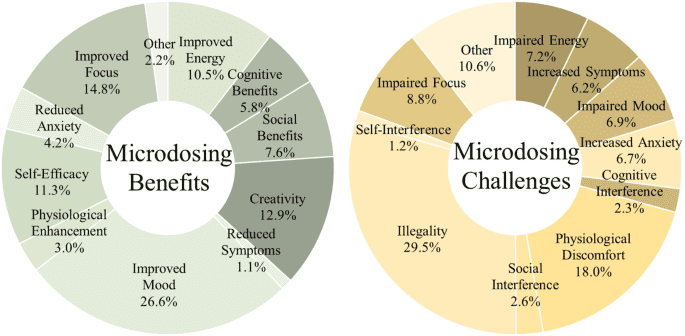
Regarding the complete intake, that is to say in perceptible doses, it is used and has proven useful in different cases: mood disorders, fear of death, addictions … The safe use of psilocybin has allowed patients to fully or partially recover, in the same way that MDMA is used in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder.The controlled framework makes it possible to reduce much of the risks while allowing the effects and the change of state to be assessed.
However, the complete intake, usually between 1 and 5 grams of dried mushrooms, can also be recreational, whether in quiet places like home, to explore the abyss of the human spirit, or in more festive places, to enjoy music and visual hallucinations.
Nevertheless, during a perceptible intake, it should not be forgotten that mushrooms have powerful effects and that there are risks that a bad experience will happen or that new side effects will appear, even to the most experienced consumers. It is therefore important to take care of your state of mind before taking and the environment in which the trip takes place.
Grow kits and different techniques
An effective and rewarding way to get hallucinogenic mushrooms is to use a home-grown grow kit. Ideal for beginners and easy to get on the net, grow kits mostly offer P.Cubensis, because they are easy to grow, and the grower can, in a short time, get a crop.
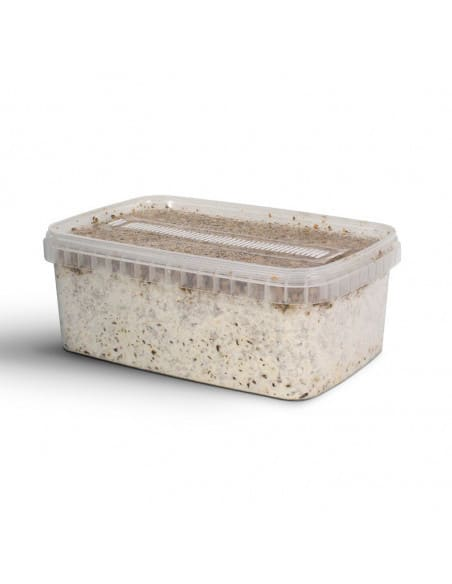

There is a list of less common kits for seasoned growers: some types of Cubensis, stronger, or other species, which can take longer to grow.
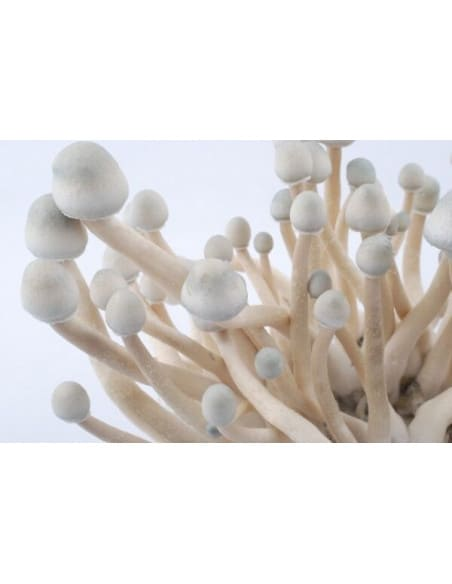

A kit can make 3 to 4 harvests on average, or even more. It can also make it possible to recover the spores of the fungi afterwards, to make your own mycelium cultures.
A second option, generally recommended if you have already succeeded in several kits, is to do everything yourself: that is, to create your own mycelium bread. For this, there are several techniques, the best known of which are PF-Tek and Monotub-Tek, which consist of inoculating grains with a strain: spores, liquid culture or a piece of mycelium…
These options cost less than kits, but require more time, technique, knowledge, rigor and energy. They also require a whole list of equipment and especially sterilization during certain stages, to avoid infections.


- Hygrometer & Thermometer

Hygrometer & Thermometer
Hygrometer & Thermometer with probe Temperature Range: -50°c ~ 70°c Measuring [...]9.00€Voir le produit - Mushroom grow kit 'Master'

Mushroom grow kit 'Master'
The Grow Kit Master includes an extra large cultivation box for bumper harvests. It can [...]54.00€Voir le produit
There are many ways, supports and potential steps to create fungi: agar, liquid culture… It is a rich, complex but accessible and fascinating world that mushroom growth!
It is also possible to pick these hallucinogenic mushrooms, depending on the country you are in. The conditions must be right and some fungi have an annual shoot, that is, they are present only once a year.
Outdoors, we can most often find Semilanceata, Azurescens or Cyanescens mushrooms, which are stronger than Cubensis, so be careful with the dosage when consuming these hallucinogenic mushrooms.

It is also necessary to be very attentive and know how to recognize mushrooms from each other.It is important to note that picking is also prohibited in many countries since mushrooms are considered narcotics.
Truffles: an alternative to magic mushrooms
“Magic truffles” are actually sclerotia. They are created from specific species of fungi (Mexicana, Atlantis, Tampanensis) and grow in the mycelium.


- Psilocybe tampanensis

Psilocybe tampanensis
Psilocybe Tampanensis is a unique strain amongst the Magic Truffles. The Psilocybe [...]13.00€Voir le produit - Psilocybe atlantis

Psilocybe atlantis
Psilocybe Atlantis was found in Fulton County, Georgia (US) and is strongly related to [...]13.99€Voir le produit - Psilocybe mexicana

Psilocybe mexicana
The Psilocybe mexicana is the best known psilocybine mushroom which also produces Magic [...]13.00€Voir le produit
They are known to have a taste that is close to that of nuts and contain mostly water when they are not dried, between 50 and 70%.To keep their psychedelic effects, fresh truffles should be kept cool and away from light. Consuming truffles causes the same effects as mushrooms because they contain the same active substances.

In some countries, the law is different from mushrooms: truffles, like mushrooms, are illegal because they are considered narcotic and in others they are not.For example, in the Netherlands, for 15 years, dried mushrooms have been banned by law, but truffles are not illegal, even if the effects are similar.
The consumption of hallucinogenic mushrooms
Although hallucinogenic mushrooms are classified as narcotics, they can have many benefits on our mental health if used safely: they can give impressive results and be used as a treatment if we remain careful when using them.
There are several modes of consumption: taking dry or fresh hallucinogenic mushroom, consumption via an infusion or the famous Lemon Tek, that is to say the mixture of the hallucinogenic mushroom with lemon juice.

Consumption by infusion, made with a tea ball or a coffee filter, reduces stomach aches. Consuming the hallucinogenic mushroom in Lemon Tek reduces the time of the onset of effects, increases the power of the trip and can also help with digestion.

However, it is possible to create resistance due to regular consumption, which is why it is preferable to wait at least 2 weeks between each intake.
Regardless of the mode of consumption chosen for hallucinogenic mushrooms, consumers are more often advised to reduce the use of hallucinogenic mushrooms to once a month, in order to integrate and understand each trip.
Cousins of Psilocybe mushrooms
We have already seen hallucinogenic mushrooms that did not contain psilocybin but there are certain types of mushrooms that are also known for their effects on the human mind, without them being part of the Psilocybe family. These mushrooms also turn blue when picked because psilocin oxidizes on contact with air.
This is the case of Pluteus Americanus, which also contains psilocybin. Nevertheless, not being consumed often, it is not known exactly if it is more potent than Cubensis.

There is also the fungus Panaeolus Cyanescens, or Copelandia Cyanescens, nicknamed Hawaiian. It contains about 2.5% psilocybin and 1.94% psilocin, so it is very potent if consumed, and is very different in appearance from P .Cyanescens. It is often available as a kit.
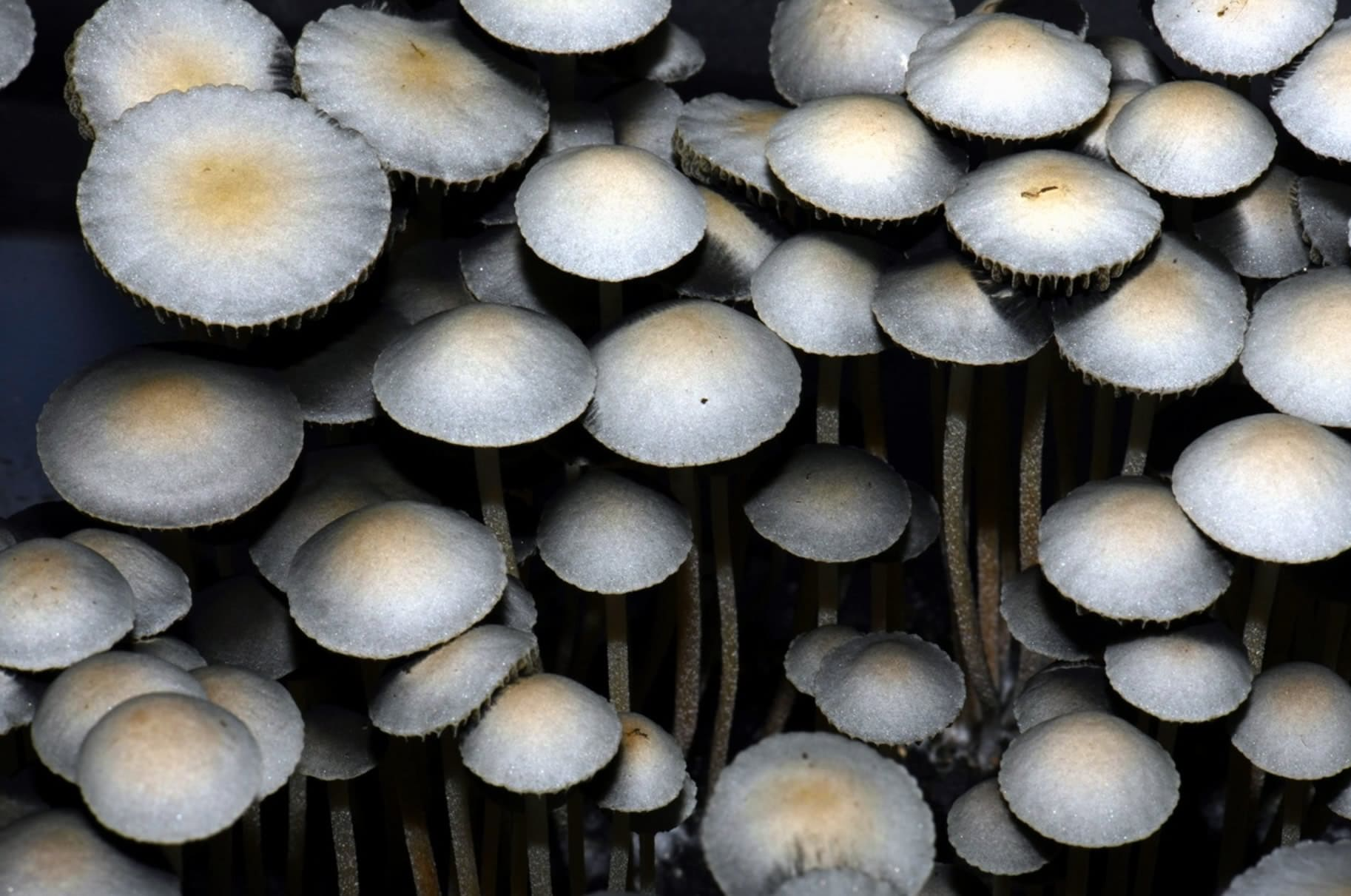

Some species of Conocybes mushrooms are also known to contain psilocybin. The fungus Conocybe siligineoides was used for shamanic purposes among some peoples of Mexico.

Finally, 14 species of Gymnopilus also contain these active substances and can cause similar effects. Most grow on the American continent or in Asia but two species are also known to grow in Europe.

In conclusion, there are a multitude of mushrooms, hallucinogenic or not, but the Psilocybe mushroom remains the best known of them. In nature or in kit, it can help some people by its therapeutic effects or offer us beautiful trips. Although it remains illegal in some countries, its history and how it acts on the human psyche remains fascinating. Although increasingly studied, we still have a lot to learn about it, like many mushrooms.