
Also known by different names depending on the languages spoken; Acacia tenuiflora Willd., Acacia Hostilis, Mimosa tenuiflora, Mimosa Hostilis, Vinho da Jurema, Jurema Preta, Jurema, Mimosa tenuiflora, Jurema Branca, M. verrucosa, Calumbi, Tepezcohuite.
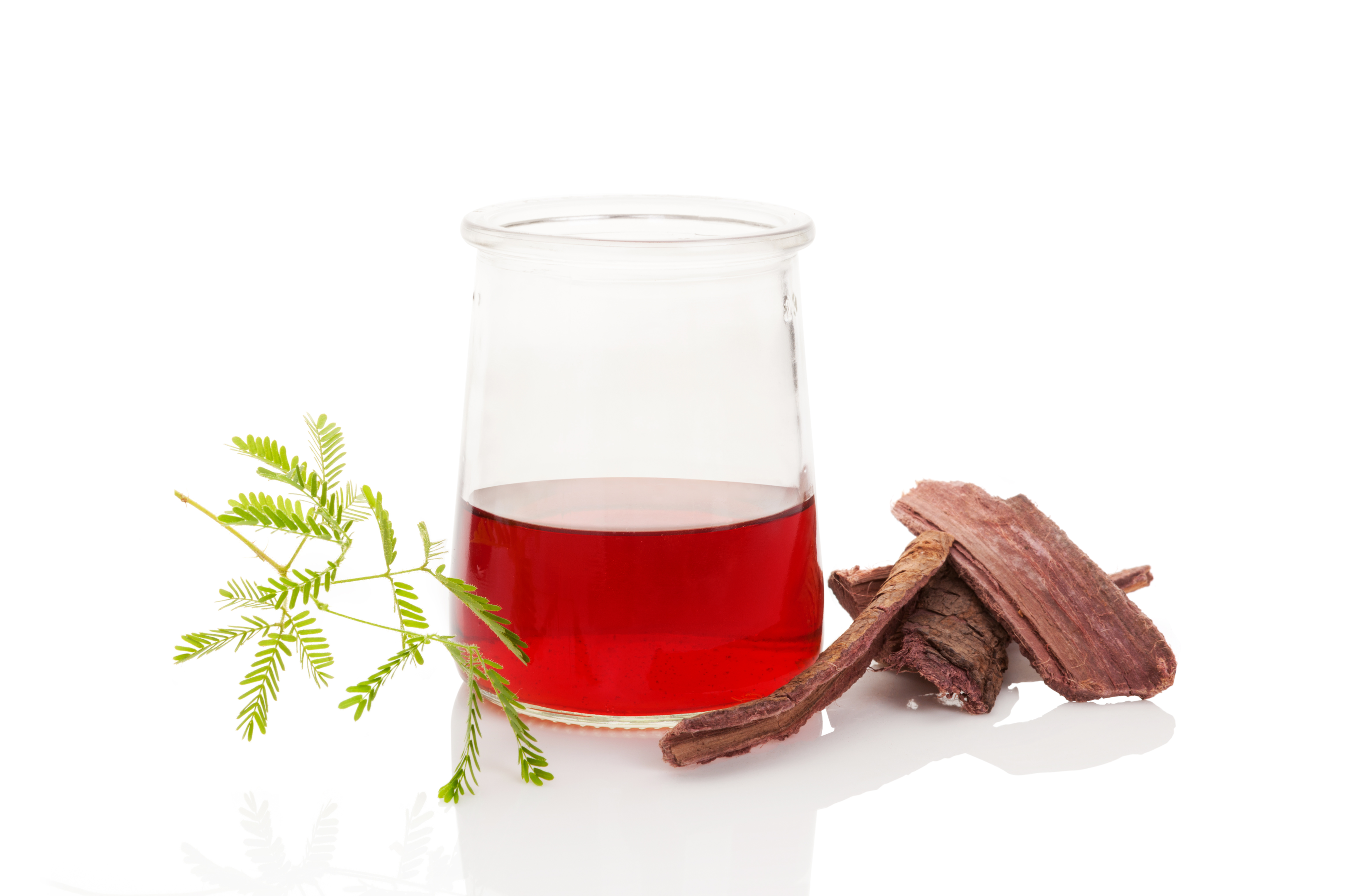
This plant is best known for its root. Once crushed, DMT, a highly prized hallucinogen, can be extracted. It is also an essential ingredient in the Ayahuasca blend (shamanic preparation with hallucinogenic properties).
In this article, all the information is provided so that anyone can make a first order of jurema preta. In short, you will know the quantity needed, its price, the doses according to the desired experience, the options offered when ordering products or derivatives of the plant, and finally where to find answers to your additional questions about ordering on the site (here). If as a result of reading this article, you still have questions send us an e-mail.

Botanical information of the plant Mimosa hostilis
The Mimosa Hostilis is part of the large family of Fabaceae. It is a small tree (also classified as a shrub) normally growing at low altitudes but can also be found at an altitude of 1000 meters. It is growing rapidly. It can reach up to 4-5 meters high in the first 5 years of life to reach an average maximum of 8m high.

Its leaves resemble those of the winter mimosa (very familiar in Europe). They are pinnate. That is to say, they have a main branch with on both sides, petioles which themselves have subleaves arranged like the barbs of a feather.
Its flowers are white and fragrant, measuring between 4 and 8 cm. In the Northern Hemisphere, it blooms and bears fruit from November to July. While in the Southern Hemisphere, it blooms from September to January, and then produces its fruit later from February to April. Its fruit takes the form of a pod. Each pod contains several oval, flat seeds.
Mimosa hostilis vigorously repels after a forest fire. This tree is said to be a pioneer plant since it is among the first species to regrow. It is an essential ally for reforestation. Once its leaves fall to the ground, they form a dense and rich carpet when transformed into hummus. In addition, Mimosa hostilis has the property of fixing nitrogen in the soil, an essential component to promote the arrival of other plant species.

Image source: gbif.org
History

Jurema has been used for thousands of years as a natural textile dye in South America. Thanks to its high concentration of tannin, it is possible to make dyes from a beautiful ochre, purple red to shades of roses.
Jurema wood is also used in construction since it is an excellent hardwood. It is for this reason that it also bears the name of “metal tree”
Where does Mimosa Hostilis grow?
Mimosa hostilis grows in virtually all of northern Brazil, but is also found in several Central and South American countries such as Venezuela, Mexico (south of Mexico), Colombia, Honduras and Panama.
Use of Mimosa Hostilis
For medicinal purposes
This plant has antifungal, antibiotic and anti-inflammatory properties. Among other things, its leaves and tea stems are used to treat a toothache. The Aztecs and other indigenous groups have used it for centuries to treat burns and other wounds. Its high tannin hold makes it astringent, giving it the ability to stop blood and help form new tissue.




Jurema also stimulates collagen production, making it an ally for healing severe wounds and burns, leaving little or no scarring.
In Brazil and Mexico, a Jurema preparation is drunk to treat headaches, respiratory diseases, or to relieve the effects of a day after a party.
For environmental purposes
The Jurema plant is used for the reforestation of forests after a fire. Its success in reforestation is due to its rapid growth and ability to fix nitrogen in the soil.
In cosmetics
Mimosa hostilis is well known in the pharmaceutical world for the manufacture of beauty products, such as soaps, shampoos, creams and many others. It is only from the 80s that have. Started serious clinical studies on its benefits. They demonstrated the connection between Jurema vino and cell regeneration, particularly in burn injuries.

Textile industry, as an exceptional dye
Vinho da jurema powder is excellent for dyeing textiles from ochre to pink to purplish. It produces park-quality dyes that it has a long-lasting hold in addition to giving fabrics vibrant colors.
For recreational purposes
Used for hallucinogenic experiences, Mimosa Hostilis powder (place your order) is used in conjunction with Peganum harmala seeds (place your order) or oral caapi extract 40:1 (place your order) as an infusion. This blend is known as Ayahuasca.

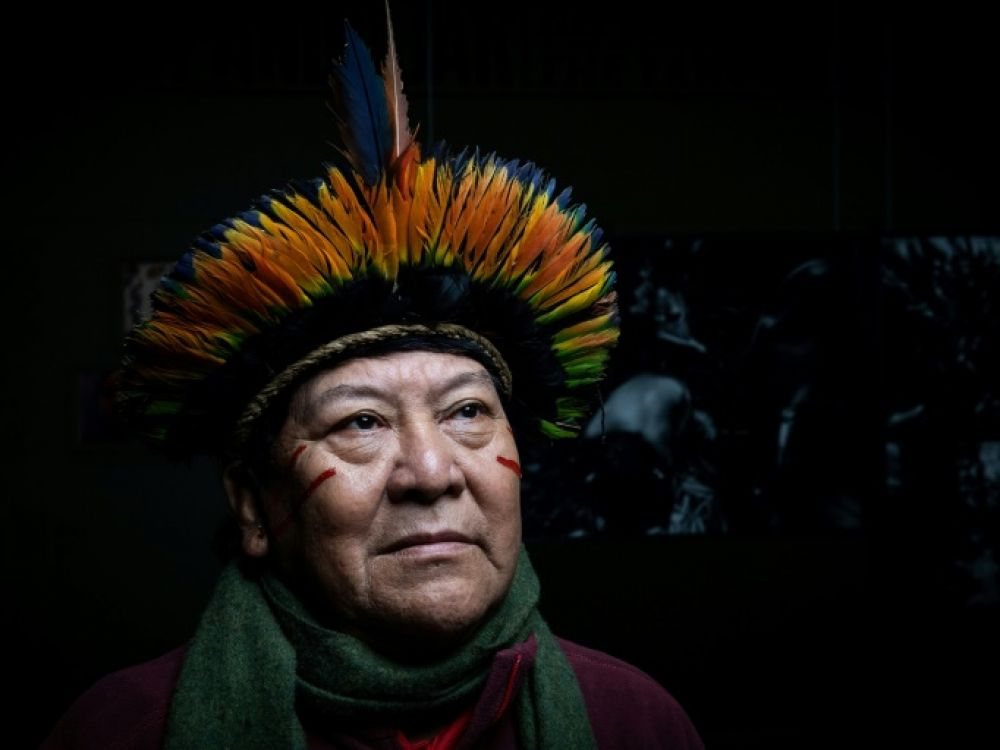
For spiritual purposes
The (powdered) root of this plant, also called MHRB (Mimosa hostilis Root Bark) has been used for a very long time by the indigenous people of Brazil and Venezuela in religious, spiritual and shamanism ceremonies. It is a tradition to consume it in the form of infusion as an entheogen (psychotropic substance that can induce a modified state). Indeed, the hallucinogenic properties of Mimosa are activated only if it is mixed with B. caapi or Peganum harmala. Otherwise, it will only have a medicinal effect. It is said of this infusion that it has the effect of healing the conscience and helping the person to overcome traumas, to bring enlightenment and to overcome depression.
 consumption" />
consumption" />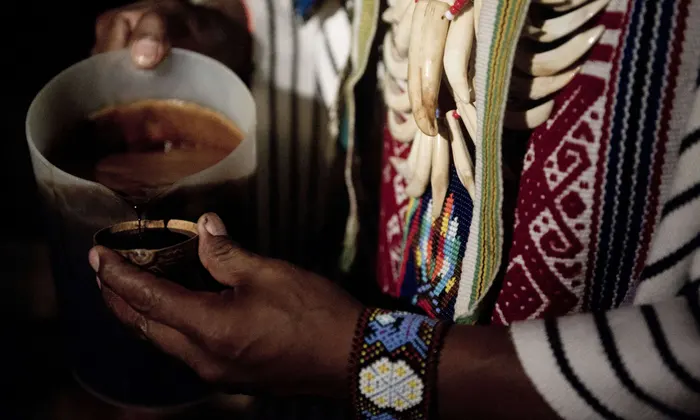
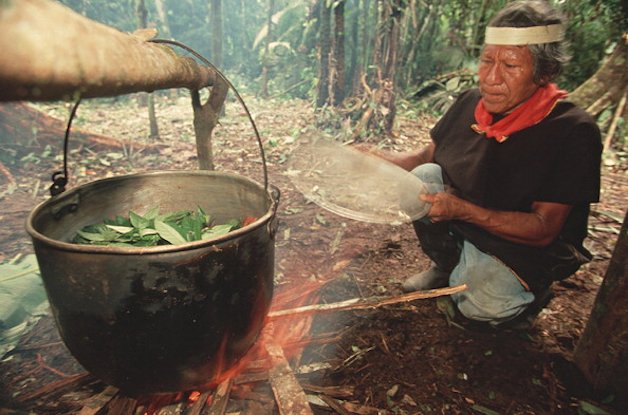



Place your order for Mimosa Hostilis powder now. Your order will arrive within a week.
How to consume it?
According to the proposed method of the Physchonaut wiki (source)
To achieve psychedelic effects, one of the most widely used options is the extraction of dmt using sodium hydroxide and naphtha. Here is the procedure to do as explained on the Physchonaut wiki site (source)
Extraction can be performed with the root bark of Mimosa hostilis (commonly abbreviated as MHRB.
Previous studies have shown that MHRB contains 0.31% to 0.57% DMT (Schultes, 1977), while the inner bark of the root contains up to 2% active alkaloids. Dried Mexican MHRB has recently been shown to have a DMT content of approximately 1%, while the stem bark has a DMT content of approximately 0.03%.
Theory
This extraction uses a traditional acid-based methodology to extract free-base DMT. This process can be summarized as follows:
The first steps (washing with vinegar and water) acidify the solution to a pH of ~4.
The vinegar then reacts with DMT in the plant material to create DMT acetate. This step is called “degreasing”.
The conversion of DMT into salt facilitates absorption by the polar solution.
Basification of the solution at a pH of 13 in the following steps extracts it from the polar solution (i.e., water) to the non-polar solution (i.e., naphtha).
The base solution reacts with DMT acetate by deprotonation to produce the pure basic form of DMT (the free base).
A high pH solution reduces the solubility of DMT. When naphtha is added, the free-base DMT is transferred to this layer of non-polar solution.
DMT is practically insoluble in this aqueous phase. Maintained at temperatures close to or at freezing, it will precipitate out of the naphtha solution by crystallization.
Risks and Hazards!!!
For an explosion to occur, there must be oxygen, an ignition source or heat and fuel (in this case, naphtha vapour).
Naphtha (Warning: Extremely Flammable)
Naphtha is a petroleum-based solvent with a strength comparable to paint thinner, but is more volatile. The volatility of naphtha means that its vapours can accumulate quickly in an unventilated space. It has a low flash point, which means it is highly flammable, behaving similarly to the lighter fluid. It can be handled safely, but it is harmful if inhaled, swallowed, or inhaled into the lungs; It is also an irritant to the eyes and skin. In case of contact with skin, wash hands thoroughly with soap will avoid irritation.
To avoid exposure, allow enough time to allow the final product to dry completely. Naphtha can be found in many hardware stores or paint stores.
Sodium hydroxide (also called lye or caustic soda) – Sodium hydroxide is very dangerous if in contact with the skin or eyes, swallowed or breathed. Eye contact can cause corneal damage or blind people, while skin contact can cause inflammation and blisters. Exposure can lead to chemical burns, as sodium hydroxide solutions can easily break down body tissues.
Exposure will leave the skin soapy and will not immediately damage the skin; Wash your hands thoroughly if this soapy sensation or irritation is felt. Wear gloves and goggles when handling this substance. When sodium hydroxide is added to the glass jar, it must be done gradually to avoid the strong exothermic reaction (heat release) that can crack the container.
Sodium hydroxide easily absorbs moisture from the air; Therefore, the container should be kept sealed when not in use. Sodium hydroxide can be found in many hardware stores and other large DIY stores.
Hardware required.
Naphtha
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), commonly known as lye
Mimosa hostilis root bark – preferably pre-shredded red, but can be shredded yourself if this option is unavailable.
Vinegar
2 L glass container
2 large pots
Glass turkey pear
Chemical-resistant gloves – Necessary to reduce the risk of dermal exposure to toxic solvents.
Chemical splash goggles – Necessary to protect the eyes from accidents that would otherwise result in direct contact with sodium hydroxide or naphtha, resulting in guaranteed vision loss.
Respirator Mask – This is vital for reducing exposure to harmful gases emitted by naphtha and laundry. Dust masks or simple surgical masks offer zero protection against naphtha vapors. The minimum NIOSH recommendation (again assuming a well-ventilated area) is a chemical cartridge respirator with … For the rest, visit: Physchonaut wiki
What is DMT?
Also called N-dimethyltryptamine (scientific term) or n dmt. DMT is a hallucinogenic drug tryptamine. This substance produces effects similar to other psychedelics such as LSD and magic mushrooms.
DMT is found naturally in plants such as Banisteriopsis cape and Psychotria viridis. The latter contains DMT while the other contains monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), which prevent certain enzymes in our body from destroying DMT. In other words, the ingestion of DMT provides psychedelic effects only when one does both the ingestion of MAOIs.
Like other psychotropic substances, DMT affects each individual in ways that are unpredictable and different for each individual. Some will say it was a beautiful introspective journey and others will have found the experience scary and too intense.
Purchases
Are you a new user of our site? Make your order on our shop with confidence. We only sell high quality MHRB from a small organic farm in Brazil.
Unlike others, the tree is not sacrificed to harvest our MHRB. Only a small part of its roots are taken to make a sustainable and conscientious culture.
Culture
For those who would be tempted to harvest all the mimosa in the neighborhood to extract DMT, well no. It’s just not the same species that ends up in your grandmother’s garden.
On the other hand, it is possible to grow the mimosa hostilis in pot. It takes several years to be able to harvest a lignified root (wooden), of significant size and ready for consumption.
Anyway, it is a beautiful decorative plant and you can also use its leaves to make a concoction against toothache.
Internal links
Add organic Mimosa Hostilis bark to your cart
https://mycotrop.com/en/smartshop/914-mimosa-hostilis-root-bark-chopped-mhrb-.html
Add a Peyote plant to your cart
https://mycotrop.com/en/smartshop/669-peyote-lophophora-williamsii-1-2cm.html

