Hallucinogenic mushrooms have become very popular lately thanks to their indoor cultivation. Many sites allow the purchase of already made cultivation kits: the grower only has to monitor the growing conditions and then harvest them. You can also buy strains of hallucinogenic mushrooms to grow your own.
Nevertheless, the first way to obtain mushrooms is to harvest them in their natural environment. Although it is also illegal in most countries, many consumers favor this method of harvesting, especially for its fun and inexpensive aspect.
Whether in its natural environment or in an artificial culture, cow dung can prove to be an excellent nutritional addition for the cultivation of hallucinogenic mushrooms. It can also be used in some kits, especially for Panaeolus Cyanescens.
Growkit Panaeolus Cyanescens Copelandia
Mycotrop SpawnBag Panaeolus cyanescens Copelandia :
Why cow dung?
Animal dung is a natural fertilizer that is used to fertilize soils: many insects and microorganisms use it as food. Insects allow the integration of feces into the soil. Cow dung is therefore an important element of ecosystem life.

In addition, cow droppings can also be used to transport and disperse seeds, while providing fertile soil. Its nutritional side makes it a good support for mushroom cultivation, but also for other types of plants and molds.
Where to find cow dung?
It is usually found in the plains: these are where the cows are left to graze. On average, a single one of them can produce up to 10 tons per year, so 50 to 60kg per day for adults. In other words, there is plenty to do!
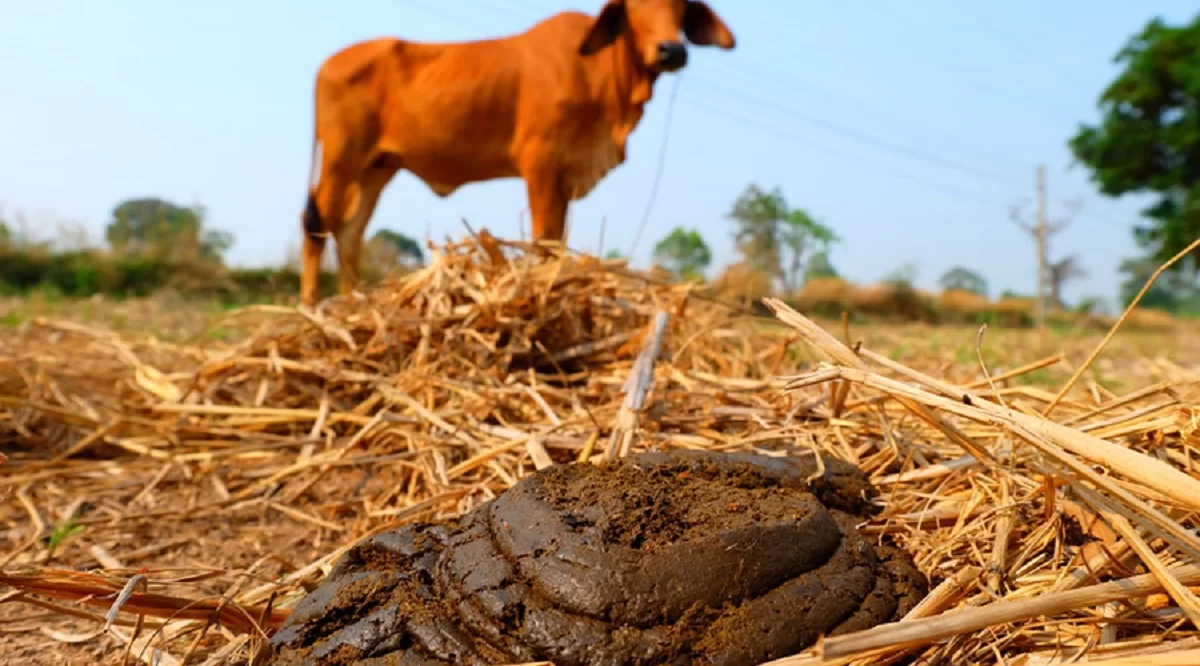

When the cows are returned, their excrement is found indoors: farmers then collect it and mix it with straw to make manure, a natural fertilizer.
Some grow kit sales sites offer bags of grain directly mixed with cow dung. These nutrient bags are more expensive, but will be able to give beautiful hallucinogenic mushrooms and are already pre-sterilized, so easy to use.
How to use it in a culture?
Cow dung is not very useful if you buy a pre-made kit, as it will sometimes already be colonized. On the other hand, if you make your own culture, you can use it. Some species of mushrooms enjoy them more than others.
In some countries, such as the United States, it is possible to buy cow dung in packages ("cow manure"). It is pre-sterilized and odorless, making it very accessible and convenient for any type of crop. It is sometimes enriched with nutrients.

If you want to use it, you must sterilize it and then add it to your nutrient base (millet, rice …), which will be colonized later. You can also use it for outdoor crops, in your garden corner.

Cow dung and gathering in the wild
As explained, cows graze and release their droppings in plains and meadows, which allows magic mushrooms to grow. However, other conditions must also be met so that these hallucinogenic mushrooms – often Psilocybe semilanceata in France – are shown: rather cool and humid weather.

These are small Psilocybe mushrooms: so you have to be careful when picking so as not to step on them. Most of the time, they do not grow on the excrement itself, but around. You also have to be careful: not all mushrooms that grow next to cow dung are hallucinogenic mushrooms.
Hallucinogenic mushrooms or not?
To avoid making a mistake, you can first compare the photos you find on the internet with your specimen. If you have any doubt, you can ask about a specialized group or page for identifying hallucinogenic mushrooms. Post a photo and wait for people's opinions. There are also some apps that can help recognize mushrooms, such as iNaturalist, but you have to be careful about their result.
It is important to note that psilocybin hallucinogenic mushrooms that grow near cow dung in pastures have a nipple on their hat: it is not a discoloration of the latter but a different shape that is formed on top. They are gelatinous and dark: the presence of these three traits generally makes it possible to identify them and eliminate other species, which are not psilocybes and do not contain psilocybin.

What hallucinogenic mushrooms can be found in cow dung?
As mentioned earlier, there are several species of mushrooms in France that cause hallucinations that can be found next to feces. Although having similar effects, the two do not contain the same active substances.
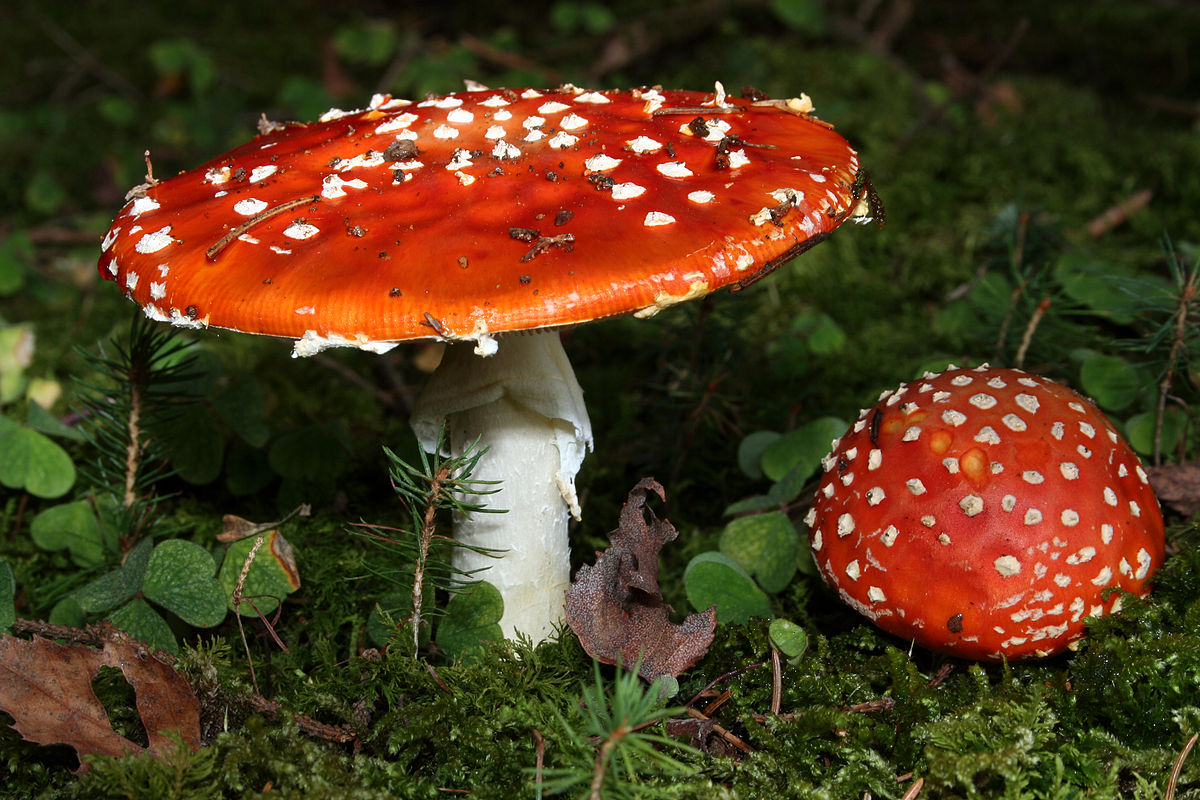
Amanita Muscaria
This fungus is better known as Amanita Tue-Mouches. It is seen in the popular imagination as a red mushroom with white spots, but its dots can disappear or move.
Its bright color makes it an easy to spot mushroom, especially since specimens are generally larger than mushrooms of the genus Psilocybe. It has a wider foot and a frill around it.

In France, it is often found in the woods, especially at the foot of birch trees. However, it can be seen in a large part of the world: it can adapt to cold climates, such as that of Siberia, but also to warmer climates, such as that of the Mediterranean basin for example.
Amanita Fly is most often confused with another similar fungus, Amanita Caesarae. The latter has a hat closer to orange and has no white dots. It is also smaller, with yellow or golden strips and a background of the same color. It can also be confused with Amanita Xanthocephala, which is only found in Australia.
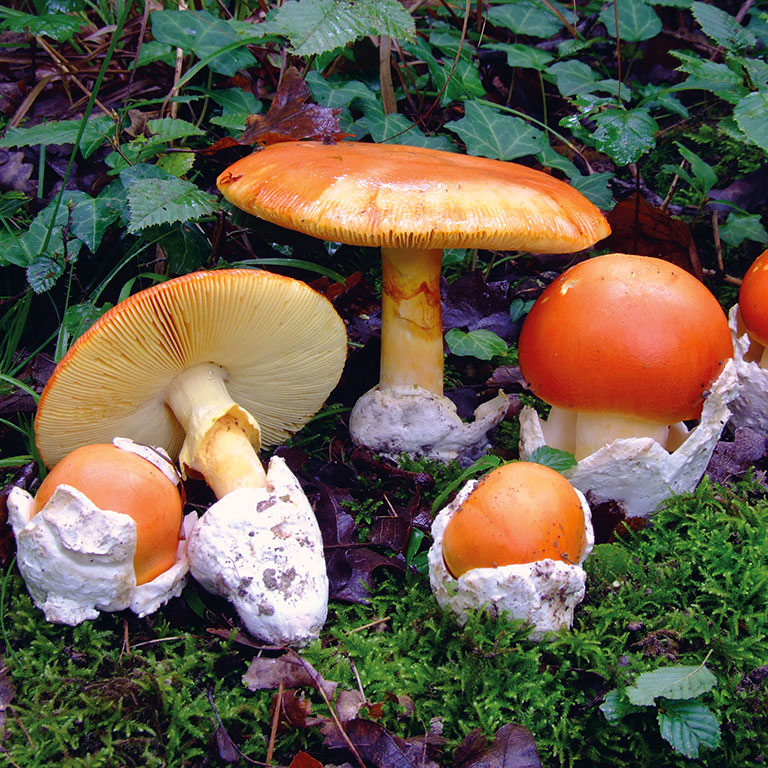
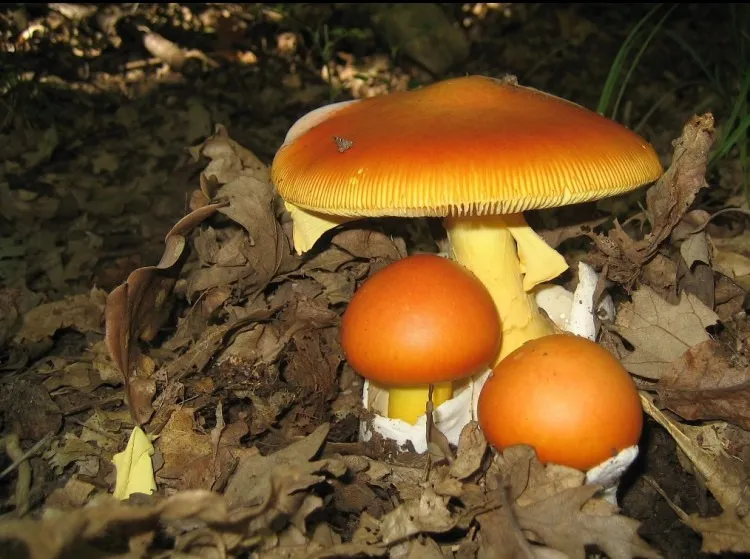


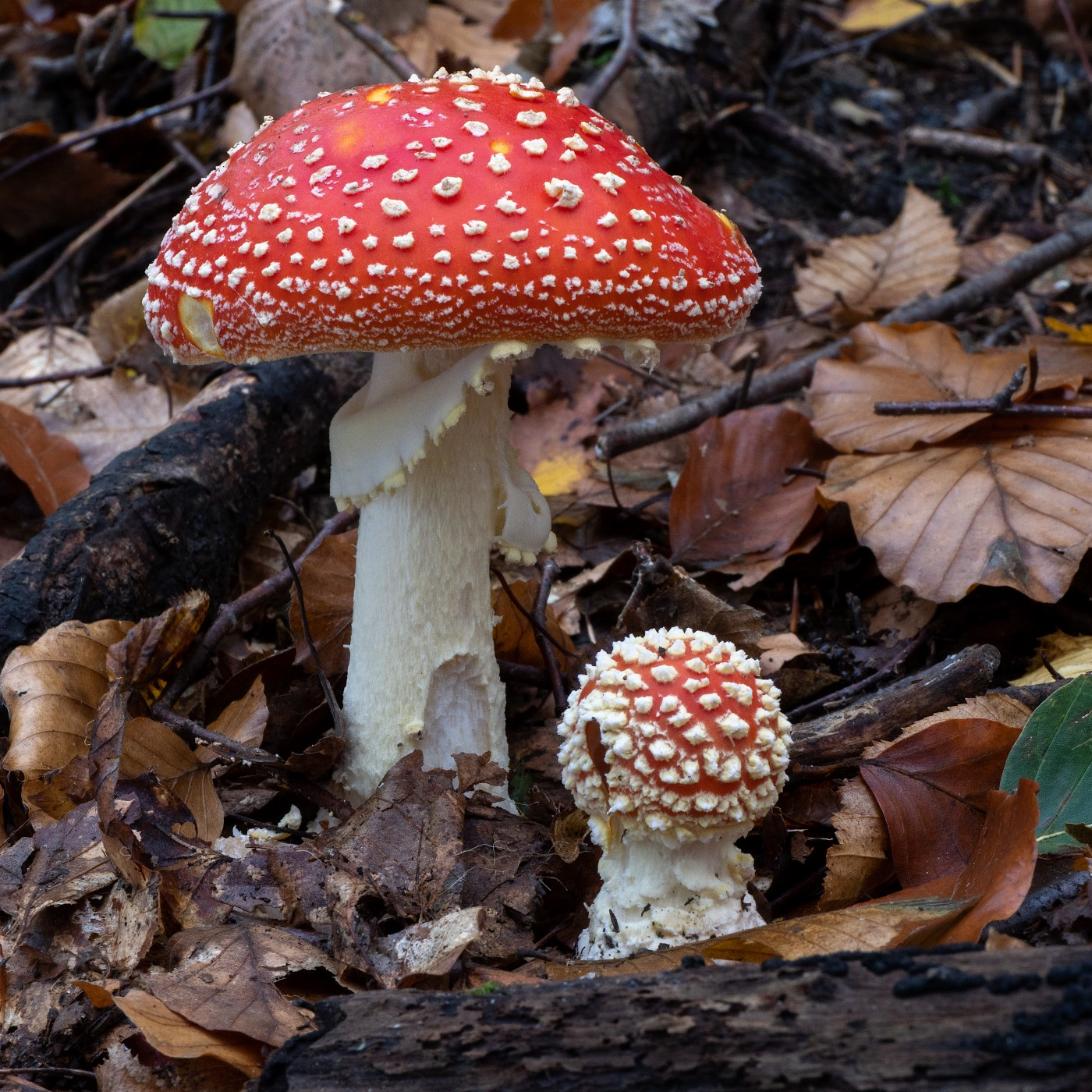
These species of fungi are known to be poisonous, but the Amanita muscaria very rarely causes deaths, sometimes hospitalization: it is rather its cousins, the Amanita phalloides, called green oronge, and the virous amanita that are very dangerous. Only half of one of his hats can cause death.


The toxic dose, with the first effects appearing, is estimated to be about a hat. The lethal dose would be around fifteen mushroom hats. The large discrepancy between the toxic dose and the lethal dose explains why the majority of people who consume it do not die from it. Nevertheless, each specimen of these species has a different concentration, so these are rough estimates.

Amanita Tue-Mouches is found in the presence of ibotenic acid and muscimole. These two substances are considered drugs: once ingested by the person, ibotenic acid is transformed into muscimole, which acts on the GABA receptors of our brain.
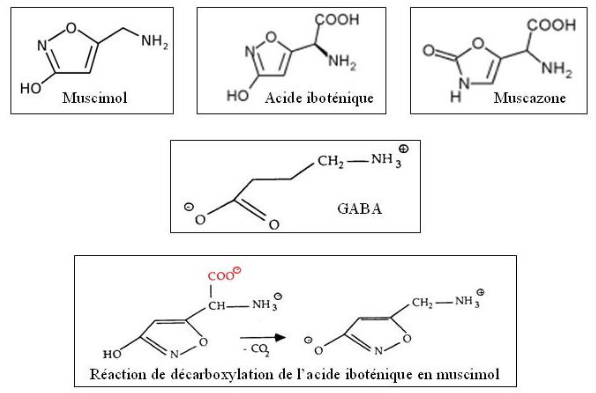
The effects and uses of Amanita Muscaria
This interaction with these receptors creates hallucinogenic or even delirogenic effects: confusion, distorted time and space, hallucinations, mood disorders… These effects are part of what is called atropinic syndrome. It also includes significant side effects: general malaise, nausea or vomiting, agitation, disorderly gestures.
Muscimole is particularly known for creating loss of attention from reality -hence its delirogenic side-, anxiety or unexplained fear and a state close to drunkenness brought with alcohol. It also increases the phases of deep sleep: someone who has consumed Amanita Muscaria will be more difficult to wake up for example.

The effects of Amanita Muscaria remain rather unpredictable and far from what we can know with other psychedelics such as LSD or Psilocybe species, which is why people do not consume it and see it as toxic, so it has little value in their eyes and is not very sought after.
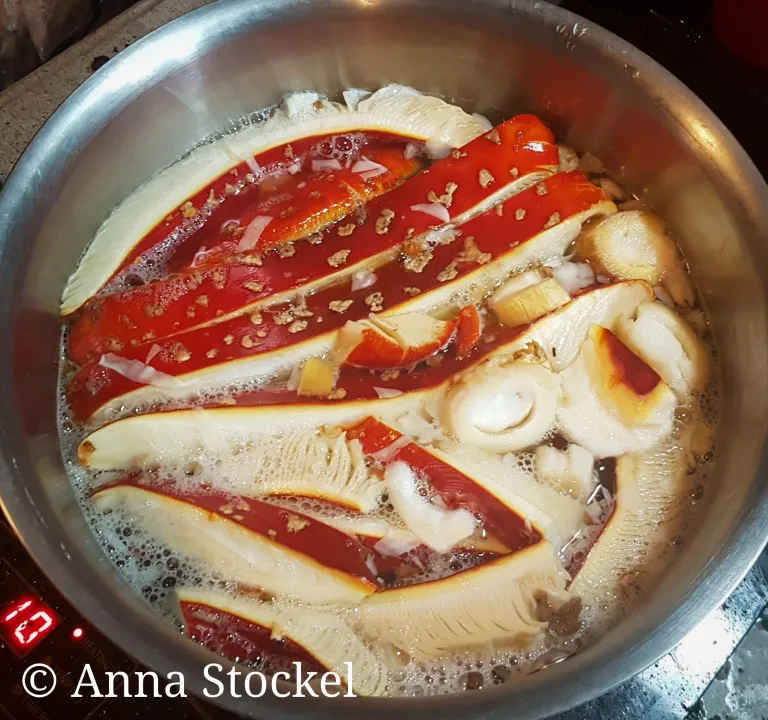
However, this mushroom has also been used for culinary purposes in different peoples, who had learned to detoxify it. There are several methods, but one of the best known is to boil it for a long time, in strips or strips, in water, the toxins being soluble. It is described as having no special taste and its consumption as a food remains marginal. In some parts of Japan, it is eaten marinated in vinegar and salted, as an accompaniment to meat.

In Siberia, it was also used for entheogenic purposes, for rituals. In Lithuania, it may have been consumed at events, such as parties or weddings. They mix it with vodka, which also acts on the same receptors. It produces sedative but also often hypnotic effects. Its consumers can have visions, hence its connection with spirituality.
It may have been used in Europe as an insecticide because, as its name almost suggests, it can lull insects, including flies, to sleep.
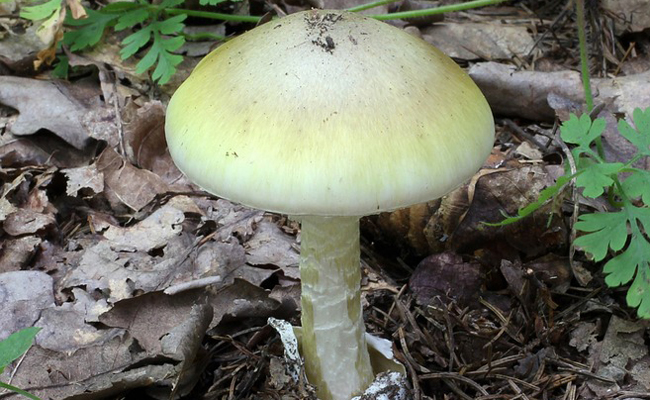
Le Psilocybe Semilanceata
This fungus is one of the mushrooms of the Psilocybes. It is a genus that also includes Cubensis, which can be found in kits for example. Fr . Semilanceata is the most common wild fungus in France, but in other countries we can find Psilocybe Azurescens or Psilocybe Cyanescens. They are two species of similar size that usually grow on wood, in a forest, near clumps but not in fields.
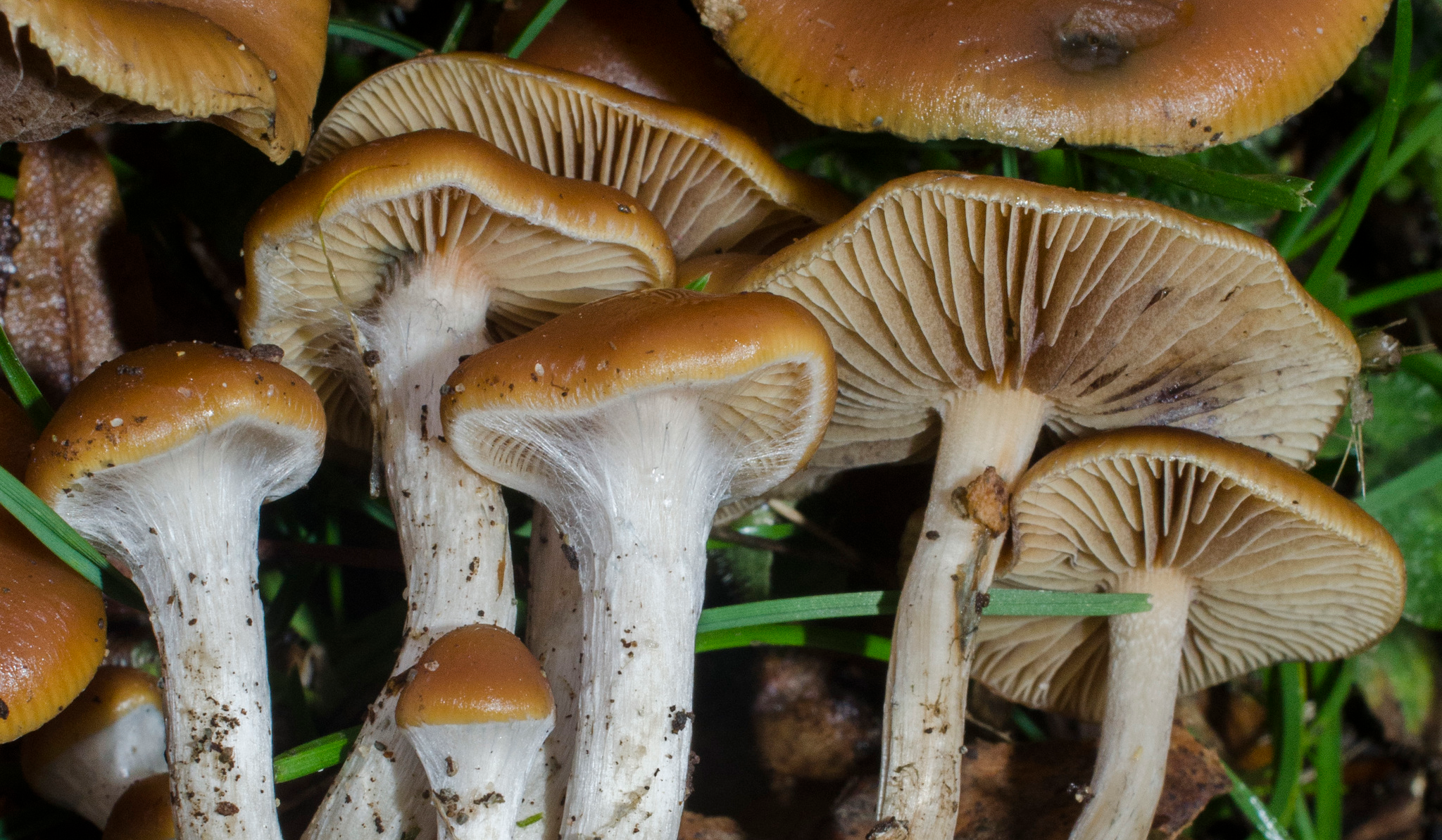


Conversely, Semilanceata is found in plains, pastures, fields, tufts of grass. Amateurs nickname it "psilo", by extension to "Psilocybe". They are more often found in a cool and humid region, for example in the Hautes Vosges, close to decaying excrement.
It is a sacrophyte fungus: it obtains its nutrients by the decomposition of organic matter. This is why it is also often found close to decaying roots, in humid places.
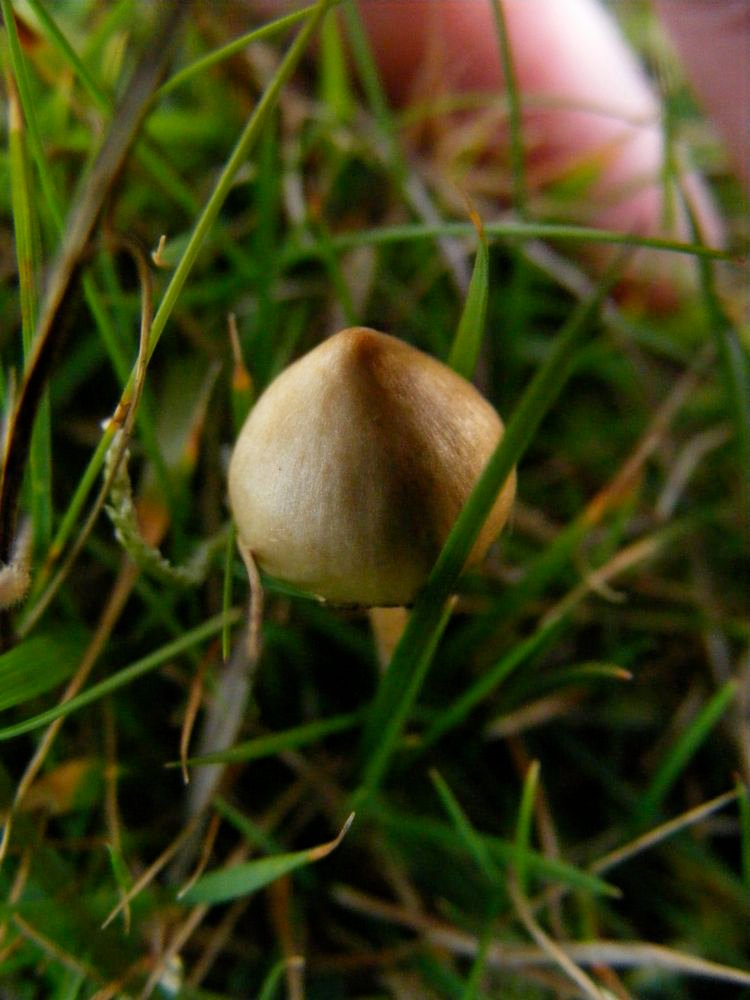

This "psilo" is recognizable by its small size and dark color, pulling towards browns. The foot of these mushrooms is thin, brown. Their hat is dome-shaped, adorned with a piece of nipple on top. Its texture is rather gelatinous and humid, due to the climate in the pastures. They are hard to find, so they may have some value.
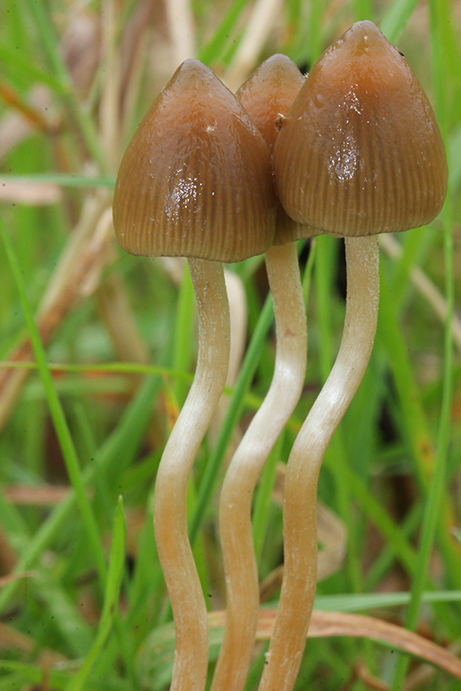

Their spores shoot towards purple-brown or deep red and can be observed under a microscope. The shape of their hat does not change during their life and a kind of frost can be observed on their surface if they are cut in half. The hat contains about twenty rather tight blades. The flesh of the mushroom is thin and dark or gray, just like the rest of the mushroom.
When damaged or handled, they take on a blue tint, which pulls towards black. This change is due to the oxidation of psilocin, one of the psychotropic substances in the fungus. In contact with air, this produces this specific effect that can be found in all mushrooms containing psilocin, including the famous Cubensis, which can be found on the pages selling kit.
His hat resembles that of the P. Mexicana, which grows in warmer and humid regions and is not found in France. The latter also appreciate soils rich in manure. It can be confused with an Inocybe Geophylla, which is lighter, pulling more towards whitish. It does not contain psilocybin, but muscarine, also present in the Amanita Tue-Mouches.
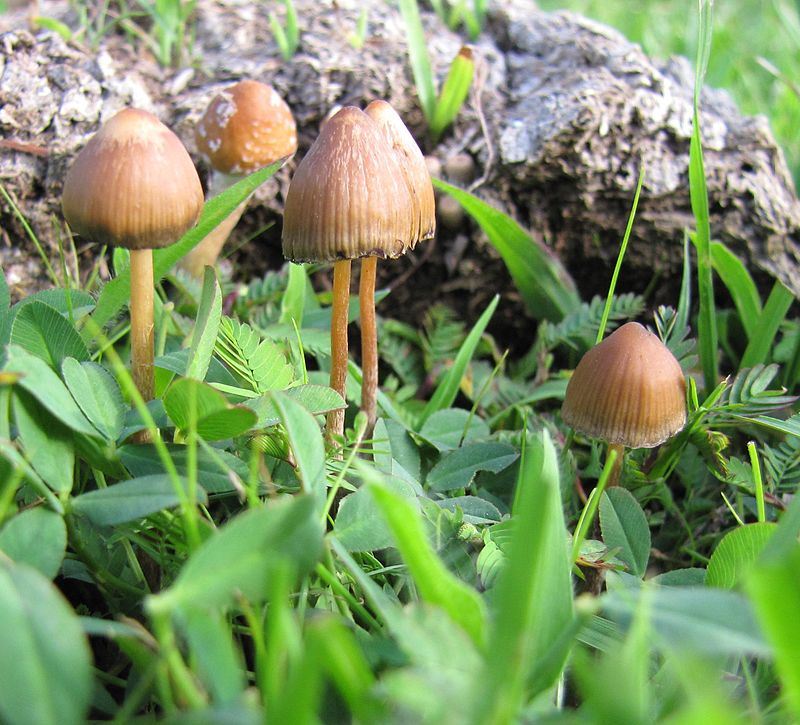

Psilocybe Semilanceata fungi may resemble other species that are poisonous, hence the warning. Psathyrella or Cortinarius Rubellus can be confused, but rather grow in the woods. It is therefore necessary to observe the photo of each specimen on the web pages and get the message across.
In France, the collection and possession of hallucinogenic mushrooms Psilocybes, even picked in the wild and French fields, are prohibited: at the key, a fine of several thousand euros, because psilocybin is considered narcotic. Some pickers have already been caught, but arrests remain anecdotal and people are rarely subject to heavy sentences.
The effects and uses of Psilocybe Semilanceata mushrooms
Fr . Semilanceata has also proven itself in studies: it has been proven by the authors that taking this fungus can be effective against Staphylococcus aureus resistant to a certain type of antibiotic. It could therefore have its place in the public health debate if this publication were to become better known.
Mushrooms P. Semilanceata are also stronger than P.Cubensis. Dried Semilanceata includes about 1% psilocybin and 0.3% psilocin. It is one of the most powerful species of Psilocybe, but also the most consistent in their level of concentration.
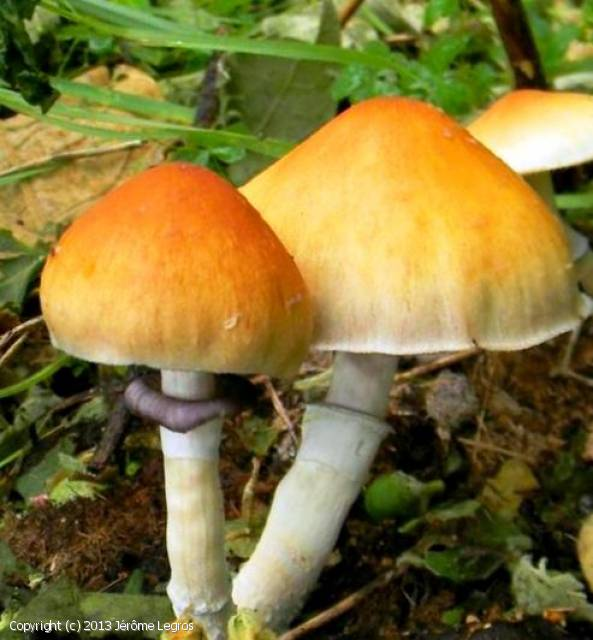

Ingestion of Psilocybe Semilanceata mushrooms causes the same effects as other mushrooms containing psilocibyne and psilocin, but at lower doses, since it is more concentrated. These effects include a change in thinking, sensory distortions and hallucinations, color saturation, altered feeling of space and time. The effect of this drug is close to that of LSD, which contains lysergic acid, which is not the same substance found in the hallucinogenic mushrooms Psilocybe.

The side effects of mushrooms are also common: nausea see vomiting, headache, disorientation, anxiety, which can lead to a "bad trip", paranoia. In order to limit them, it is advisable to create an environment where the traveler feels safe, surrounded by people he knows and trusts.
Whether for Semilanceata or other psychedelics, it is best to take a small dose and increase gradually, if it suits the user. Avoid places or situations that are too unforeseen, which could cause sudden anxiety. A "trip-sitter" is recommended, especially if it is a first for the person who consumes mushrooms or if he is the object of anxiety. This person – usually sober – will be able to help and accompany the consumer in his journey and support him in case of problems.
For more seasoned consumers and looking for thrills, Semilanceata can be consumed in "lemon tek", i.e. mixed with lemon juice. This technique makes it possible to metabolize the active substances faster: the climb is shorter but the journey is also much more intense. Lemon juice can help reduce nausea and stomach aches.
Other animal feces
They are often put in some grow kits. Copelandia kits often contain horse dung in part. Copelandia mushrooms, whose real name is Panaeolus Cyanescens, require slightly different growing conditions from Psilocybe Cubensis mushrooms. They require a slightly higher temperature and more humid air. It is also generally advisable to let the mushrooms grow well and to harvest them when the spores are released, unlike the Cubensis.

Their substrate is made of manure, therefore a mixture between straw and horse dung: this makes it possible to reproduce their natural environment. The mushroom kit arrives at the grower, totally colonized, and will allow him to harvest mushrooms up to 5 times more powerful than Cubensis. The fruiting time is usually between 5 and 7 days. These mushrooms are thin and slender. The center of their hat is tinged with gold but the rest is rather light. Because of their potency, it is not necessary to apply the same dosage as with other mushrooms, but go little by little and test in several times.
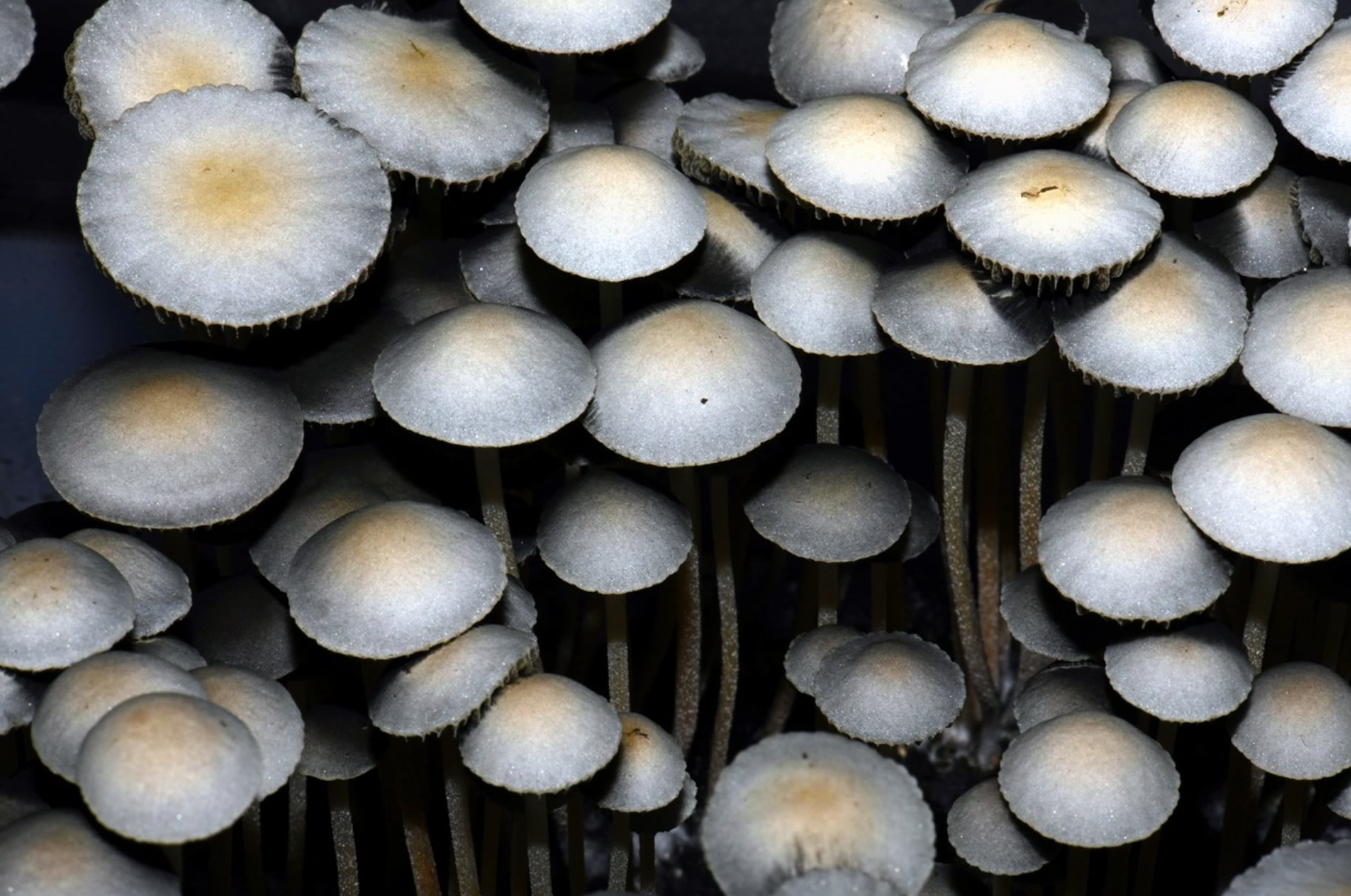

Psilocybe Semilanceata mushrooms can be found in pastures and have a small dark cap with a nipple. The Amanita Muscaria find their origin rather in birch woods. Psilocybe, Amanita or Panaeolus are mushrooms that can use cow or horse dung as a nutrient base for later growth.
Dung is sometimes added to kits for specific species, but it can also be used for homemade, indoor or outdoor crops. This may increase the yield and give it the necessary nutrients. We might as well use what nature offers us for free!

